Flexibility and efficiency are keys to success in today’s fast-paced business landscape. Business leaders constantly look for ways to improve both while keeping an eye on the bottom line and reducing security risks. One trend that has steadily grown in prominence is the adoption of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies.
As the digital workforce continues to evolve, more small and mid-sized businesses are embracing BYOD solutions as a way to reduce costs, improve employee satisfaction, and boost employee productivity. But, as appealing as BYOD may be, personal devices used for work-related business present a unique set of security challenges. This article will simplify BYOD security solutions and provide best practices for entrepreneurs looking to adopt or improve their BYOD strategies.
The Double-edged Sword of BYOD: Benefits and Risks
When adopting a BYOD policy, business leaders must consider both benefits and risks to ensure employees can efficiently perform their duties while also safeguarding corporate data. A comprehensive BYOD security policy is essential to address potential BYOD security risks.
Advantages of Adopting a BYOD Policy
Perhaps the top three benefits of implementing a BYOD policy are cost savings, increased productivity, and enhanced employee satisfaction.
Cost Savings
One of the main drivers behind the widespread adoption of BYOD is the potential for cost savings. With employees using their personal devices for work, companies can significantly reduce hardware investments. Purchasing and maintaining corporate devices can be a significant expense, especially for startups and small businesses. Organizations can minimize these costs and focus resources elsewhere by allowing employees to use their personal devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Increased Productivity
Reduced cost isn’t the only benefit of a strong BYOD strategy. BYOD can lead to increased productivity. A study conducted by Dell in 2020 found that companies with BYOD policies saw a whopping 69-percent increase in productivity. It makes sense. Employees are often more efficient when using devices they know well, and the convenience of using one device for both work and personal matters can help them stay connected and responsive no matter where they are. With the rise of remote work and flexible work arrangements, this ability to remain productive across locations is invaluable for the modern business landscape.
Employee Satisfaction
Finally, BYOD can also foster greater employee satisfaction. Several studies have found that many employees prefer working on devices they are already familiar with. Whether it’s the operating system, software, or overall user experience, allowing employees to use their own personal devices creates a more comfortable work environment. The flexibility and autonomy that BYOD policies provide allow employees to work more comfortably and manage their work-life balance better.
Inherent Security Risks and Challenges
Despite its benefits, BYOD poses significant security risks that should not be underestimated. Understanding these BYOD security risks is crucial for implementing effective corporate data security measures.
Threat of Data Breaches
One of the primary concerns is the potential for leaked sensitive data. Personal devices are often less secure than company-issued devices, making them more vulnerable to hacks, malware, and unauthorized access. If a compromised personal device is used to access corporate data, a costly security breach could occur. The risk of data theft increases when employees’ personal devices are not properly secured.
Decreased Network security
Employees’ personal devices connecting their personal devices to the corporate network can expose the company to threats if their devices are not adequately secured. Unsecured devices, unpatched software, and the absence of security protocols on personal devices can all open doors to cybercriminals looking to exploit weak entry points. Ensuring proper network connectivity and implementing strong security controls are essential to mitigate these risks.
Compliance Concerns
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific security standards also becomes more complex in a BYOD environment. For companies handling sensitive or regulated data, ensuring that personal devices comply with legal and regulatory requirements is essential to avoid fines and reputational damage. This includes implementing measures to protect data and prevent data leaks of business data and company’s sensitive data.
Key Components of a Robust BYOD Security Policy
Despite the obvious security risks associated with BYOD, SMBs can roll out a successful BYOD strategy as long as proper policies and technology are in place and employees are educated about the security concerns associated with BYOD security.
Clearly Defined Guidelines
A successful BYOD policy begins with clear, comprehensive guidelines. Establishing rules for device authorization, acceptable use, and security requirements is essential to mitigate risks. Employees should be fully aware of which BYOD devices are permitted, what is considered acceptable work use, and the necessary security measures they must implement on their personal devices. Using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication or two-factor authentication, implementing mobile device passcodes, and enabling device encryption are policies that can be controlled with BYOD and add an extra layer of security.
Balanced Privacy and Security
Striking a balance between privacy and security is another important consideration. While companies must monitor and manage devices accessing their networks, they must also respect employee privacy. Policies should clearly outline what kind of monitoring will be conducted and ensure that it does not infringe on personal privacy.
Updated Policies
Regular policy updates are also crucial. The technology landscape is constantly evolving, as are cybersecurity threats. Companies must review and update their BYOD security policies frequently to remain relevant and effective. This should include keeping track of new device types, operating system updates, and emerging threats to address potential vulnerabilities before they become problems. Ensuring device security through regular updates and latest security patches is crucial for maintaining a secure BYOD environment.
Technological Foundations of BYOD Security
Comprehensive Risk Assessment
Before implementing a BYOD policy, conducting a thorough risk assessment is essential. This process involves evaluating the risks that BYOD introduces to the company’s network, data, and overall security posture. Factors to consider include the types of BYOD devices employees will be using, the sensitivity of the data being accessed, and the company’s capacity to respond to security incidents. Identifying these risks upfront allows for better planning and implementation of security measures tailored to the organization’s needs.
Essential Security Tools and Solutions
Several tools and technologies are vital to creating a secure BYOD environment. These BYOD solutions help address various aspects of device security and data protection.
Data Encryption and Data Loss Prevention
Data encryption and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions are essential for protecting enterprise data. These tools ensure that the data remains inaccessible to unauthorized users even if a device is lost or stolen. Encrypting data on mobile devices and implementing DLP can significantly reduce the risk of data leakage.
Mobile Application Management and Mobile Device Management
Mobile Application Management (MAM) and Mobile Device Management (MDM) systems play a critical role in BYOD security. MAM focuses on managing and securing the personal applications that employees use for work, while MDM provides comprehensive device management capabilities, allowing companies to enforce security policies, track devices, and remotely wipe data if necessary.
MAM allows organizations to manage work-related applications on employees’ personal devices without managing the entire device. For example, a healthcare provider could allow doctors and nurses to use their personal devices to access corporate data in a secure medical records application containing sensitive patient information. To maintain security, however, the organization would require the user to use MFA to access the app. It would also enable encryption to protect patients’ personal health information (PHI).
Containerization
Containerization is another effective solution, as it separates personal and corporate data on the same device. Many MDM solutions use containerization to isolate corporate data from personal apps, files, and photos. This approach ensures that sensitive company data remains secure, even if the employee’s personal use of the device is less secure.
A containerization setup also allows IT administrators to remotely manage the containerized environment without affecting the personal side of the device. Security policies, such as data encryption and password enforcement, can be enforced in the corporate container. And if a device is lost or stolen, data from the container can be remotely wiped without affecting personal information. This is particularly important for managing lost or stolen devices and stolen device scenarios
Virtual Private Networks
Lastly, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are vital for secure remote access. Employees should never access the company network via public Wi-Fi. Connecting to the corporate network through a VPN ensures that their data is encrypted and protected from potential threats. This is crucial for maintaining corporate data security when employees access corporate resources from various locations.
Emerging Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming increasingly important in BYOD security. AI can help companies detect unusual or suspicious behavior in real time, while machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential security threats before they cause harm. These technologies can enhance device security by providing advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
5G and Internet of Things
The rise of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) is also impacting BYOD strategies. With faster data transfer speeds and more connected devices, 5G and IoT increase the complexity of securing BYOD environments. However, these technologies also offer new opportunities for enhanced security measures, such as real-time monitoring and automated threat responses. This is particularly relevant for managing Android devices and implementing Android Enterprise solutions in a BYOD context.
Real-World BYOD Security Solutions: A Comparative Review
Several BYOD security platforms are available on the market, each offering unique security features to help businesses protect their networks and data. Leading solutions include VMware Workspace ONE, Microsoft Intune, and Cisco Meraki. These platforms provide comprehensive BYOD solutions that address various aspects of device management and data security.
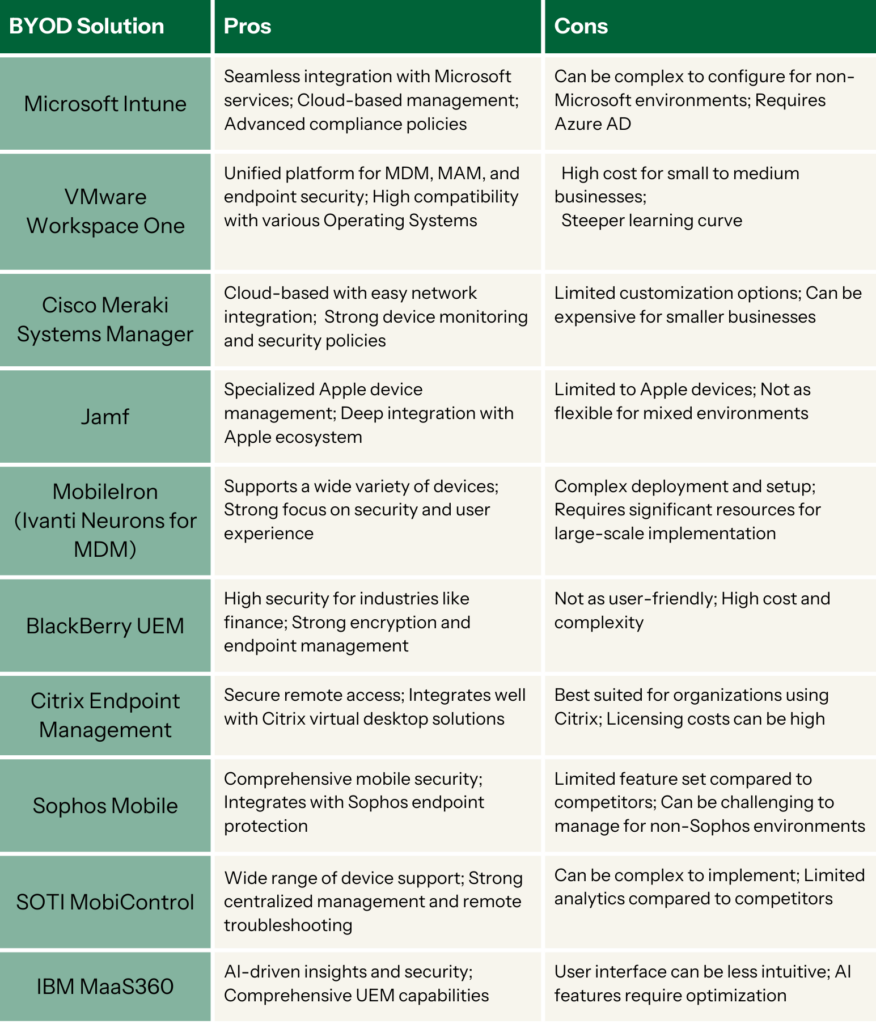
Comparing these solutions based on features, usability, and pricing can help entrepreneurs select the best fit for their business needs. Smaller businesses may prefer more affordable, user-friendly options, while larger organizations may require more robust and scalable BYOD solutions. It’s important to consider how these solutions handle personal computers, mobile devices, and other types of BYOD devices used within the organization.
Implementing BYOD: Steps for Business Owners and IT Teams
Stakeholder Buy-in
Successful BYOD implementation requires collaboration between business owners, IT teams, and employees. Stakeholder and employee engagement is critical from the start. Involving employees in the policy creation process can help identify potential issues and ensure buy-in. This collaborative approach can help address concerns about personal use of devices and how it intersects with work-related activities.
Security Awareness Training
Training programs are essential for educating employees on the importance of security and how to protect company data on their personal devices. Regular security awareness training can help reduce the risk of breaches caused by human error. Educating employees about the role of using multi-factor authentication and strong passwords in preventing sensitive data leaks can foster a strong cybersecurity culture within the organization. These security programs should cover topics such as device security, data protection, and best practices for personal use of devices in a work context.
Security Audits and Incident Response Plans
Conducting regular security audits and developing a comprehensive incident response plan are also vital steps. Security audits help identify vulnerabilities in the BYOD environment, while an incident response plan ensures that the company is prepared to respond quickly and effectively in the event of a security breach. Security teams should be prepared to handle various scenarios, including lost or stolen devices and potential data leaks.
Common Questions About BYOD Security
What Kind of Technical Support Should You Offer for Personal Devices?
Offering adequate technical support for personal devices is crucial. Companies should provide guidelines for troubleshooting common issues and set up help desk services specifically for BYOD-related queries. It’s also important to define the level of support employees can expect, as it may not be feasible to fully support every personal device. This support should cover various device types, including personal computers and mobile devices.
What Happens to Company Data if an Employee Leaves or Loses Their Device?
When employees leave the company or lose their devices, remote wiping capabilities will safeguard company data. MDM solutions allow businesses to wipe corporate data from personal devices without affecting personal information, ensuring that sensitive information doesn’t fall into the wrong hands. This is particularly important for managing stolen devices scenarios and preventing unauthorized access to corporate systems.
How Can We Measure the Success and ROI of Our BYOD Program?
To measure the success and ROI of a BYOD program, businesses should track key metrics such as employee productivity, cost savings on hardware, and incident rates related to security breaches. Regularly reviewing these metrics can help fine-tune the program and ensure it continues to deliver value. This analysis should also consider the impact on network access, user access to corporate resources, and overall corporate data security.
What Industries Can Implement BYOD?
BYOD policies can be implemented across various industries, from tech startups and creative agencies to healthcare and finance. However, businesses in regulated industries such as healthcare must take extra precautions to comply with laws like HIPAA while ensuring that security remains a top priority. These industries often need to implement stricter measures to restrict access to sensitive information and prevent data leaks.
Conclusion
BYOD offers significant benefits but requires a proactive approach to security. By following best practices and adopting the right tools, entrepreneurs can leverage BYOD to drive growth while safeguarding their businesses from potential security risks. Implementing robust BYOD security solutions helps organizations balance the advantages of employee-owned devices with the need to protect corporate data and maintain a secure IT environment.