Data has become the lifeblood of modern business operations, enabling decision-making, customer engagement, and overall efficiency. However, the increasing reliance on data also brings heightened risks. Cyberattacks, natural disasters, and human error threaten business continuity, emphasizing the need for robust data backup strategies. Modern corporate data backup systems must protect against cyber threats, phishing attacks, and other evolving risks that could lead to major data loss. Outdated methods like physical storage devices fail to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced, interconnected world, making a comprehensive approach essential.
Corporate data backup is not just about copying files but about ensuring business resilience, aligning with compliance requirements, and protecting against emerging threats. As we move into 2025, the landscape of data protection is more dynamic than ever, demanding solutions that are scalable, secure, and seamlessly integrated with modern IT infrastructures.
Understanding Corporate Data Backup in the Modern Business Landscape
What is Corporate Data Backup?
Corporate data backup involves creating copies of business-critical information to ensure its availability in case of data loss or corruption. This process safeguards operational continuity, protecting sensitive data from threats ranging from cyberattacks to hardware failures. Data backup is no longer a luxury but a fundamental requirement for every organization.
In practical terms, data backup ensures that every piece of critical information—from customer records to internal communications—remains accessible even during unexpected disruptions. Organizations must evaluate the types of data they handle, their value, and the potential risks of losing access to this information to develop an effective backup strategy. Implementing regular backups and utilizing advanced backup technology provides an essential layer of protection for organizational data.
The Evolution of Data Backup: From Physical to Cloud Solutions
Traditionally, businesses secured their data using physical storage methods such as tapes and external drives. While effective in their time, these methods were cumbersome, prone to damage, and limited in capacity. Modern solutions, particularly cloud-based systems, revolutionize data backup by offering scalability, accessibility, and enhanced security. Cloud solutions eliminate geographical constraints and provide near-instantaneous data restoration, meeting the demands of today’s digital environment.
The shift from physical to cloud solutions reflects the broader digital transformation of businesses. Cloud storage allows companies to move beyond the limitations of physical storage—such as vulnerability to fire, theft, and natural disasters—and embrace flexible, automated systems that adapt to changing business needs. Moreover, cloud solutions facilitate collaboration and remote access, critical features for modern workflows.
In addition to the transition to cloud solutions, businesses now utilize various types of backup methods, each suited for specific needs:
- Full Backups: This method creates a complete copy of all data at a given point in time. While full backups are time-consuming and require significant storage space, they provide the most straightforward recovery process. They are ideal for initial backups and periodic full-system restorations.
- Differential Backups: This approach captures changes made since the last full backup. Differential backups are faster than full backups and require less storage, making them a practical option for businesses needing frequent updates without the time investment of full backups. However, recovery involves the last full backup and the latest differential backup.
- Incremental Backups: This method saves only the changes made since the last backup of any kind (full or incremental). Incremental backups are the fastest and least storage-intensive but require sequential recovery steps, making the process more complex. They are ideal for businesses needing frequent backups with minimal resource use.
Combining these methods allows organizations to balance speed, storage efficiency, and recovery simplicity. For example, a weekly full backup supplemented by daily incremental backups offers a strategic mix of comprehensive coverage and efficiency.
The Importance of Data Backup for Business Continuity
Data backup is integral to business continuity planning. It ensures that operations can quickly resume following disruptions, minimizing downtime and financial losses. Businesses that prioritize robust backup strategies are better equipped to maintain customer trust and comply with regulatory requirements, positioning themselves for long-term success.
In addition to ensuring operational continuity, businesses must recognize the types of data that are most critical for backup. For example, financial records such as payroll data, tax information, and transaction histories are essential for compliance and day-to-day operations. Customer data, including personal details, purchase histories, and communication records, is equally crucial as it directly impacts customer trust and engagement. Other vital categories include intellectual property, employee records, and sensitive operational data, all of which support core business functions.
Business continuity relies not only on having backups but also on ensuring that these backups are functional and up-to-date. Regularly testing restoration processes can reveal weaknesses in backup strategies and ensure preparedness for real-world scenarios. For instance, a retail business that frequently updates its product database must ensure daily backups to avoid losing valuable sales and inventory information. Similarly, healthcare organizations must safeguard patient records through frequent backups to comply with HIPAA regulations and provide uninterrupted care.
Comprehensive Corporate Data Backup Solutions in 2025
Cloud Backup Solutions: Features and Benefits
Cloud backup solutions dominate the corporate landscape due to their reliability, scalability, and security features. Cloud solutions offer:
- Encryption: Ensures data is secure during transmission and storage.
- Redundancy: Replicates data across multiple locations to prevent loss.
- Cost-effectiveness: Flexible pricing models cater to businesses of all sizes.
- Scalability: Adapts to growing storage needs without significant upfront investment.
The value of cloud backups extends beyond mere storage. These solutions enable businesses to implement disaster recovery plans, ensuring rapid access to data during emergencies. Modern backup software helps organizations automate their digital backups, making it easier to maintain an entire backup of critical systems. For example, a financial institution can rely on cloud backups to restore customer transaction histories within minutes, preserving customer trust and operational stability.
A word of caution: While some of the leading cloud-based solutions, such as AWS or Microsoft Azure, offer backup solutions, they do not guarantee their backups and actually state that the customer is responsible for correctly setting up backup policies and testing them. Additionally, performing a full restore from one of the public cloud solutions can run into thousands of dollars. A better solution would be to work with a private cloud provider like MIS Solutions.
On-premises and External Hard Drive Options
While cloud solutions are popular, on-premises systems and external hard drives still have roles in data backup strategies. On-premises solutions offer complete control over data but require significant investment in hardware and maintenance. External drives and Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices provide convenient local backup options but are susceptible to physical damage and theft. Businesses must weigh these options against their specific needs and risks.
For example, companies operating in regions with limited internet connectivity might prefer on-premises solutions to ensure uninterrupted access to backups. However, combining on-premises storage with cloud backups can provide a balanced approach, leveraging the strengths of both methods.
Evaluating Backup as a Service (BaaS) Providers
Backup as a Service (BaaS) providers offer managed solutions that alleviate the burden of maintaining backup systems in-house. When selecting a BaaS provider, businesses should consider:
- Reliability and uptime guarantees: Ensure continuous access to backups.
- Support and service-level agreements (SLAs): Provide clarity on response times and responsibilities.
- Integration with existing systems: Avoid compatibility issues.
- Customization options: Tailor solutions to unique business requirements.
Top BaaS providers include Veeam, Carbonite, and Acronis, each offering unique features tailored to different organizational requirements. Businesses should also evaluate provider reputations, read reviews, and request demonstrations to ensure alignment with their needs.
Note: While these services do offer effective backup solutions, the customer is ultimately responsible for performing any restores necessary.
Designing an Effective Corporate Data Backup Plan
The 3-2-1 Backup Strategy Explained
The 3-2-1 backup rule and 3-2-1 backup strategy remain cornerstones of effective data backup planning. It involves:
- Maintaining three copies of data.
- Storing them on two different media types.
- Keeping one copy offsite.
Implementing this strategy ensures redundancy and resilience against localized data loss events. For instance, a mid-sized business might use on-premises storage, cloud backups, and an external hard drive stored offsite.
Real-world applications of the 3-2-1 strategy include government agencies safeguarding critical citizen records. By keeping multiple backups in diverse formats and locations, they ensure uninterrupted services even during natural disasters or cyberattacks.
Regular and Automated Backup Schedules
Automation is key to ensuring consistent and reliable backups. Businesses should:
- Schedule backups during off-peak hours to minimize disruptions.
- Use tools like Commvault, Veeam or Acronis for automated workflows.
- Set frequency based on data volatility, with critical systems backed up hourly and less critical data backed up daily or weekly.
Tools like backup monitoring dashboards allow businesses to track backup health in real-time. These systems can send alerts for failed backups, enabling IT teams to address issues promptly and avoid data loss.
Balancing Storage Needs with Cost-Effectiveness
Analyzing storage requirements helps businesses avoid overprovisioning. Tiered storage solutions, such as combining high-speed SSDs with cost-effective cloud options, can optimize costs without compromising performance. Regular audits of storage usage can uncover opportunities for cost savings.
By categorizing data based on its importance and frequency of access, businesses can allocate resources more effectively. Critical data can be stored on premium storage solutions, while less critical archives can utilize economical options.
Incorporating Physical Copies and Offsite Storage
Physical backups remain relevant in certain scenarios. Storing copies on tapes or external drives in a secure offsite location can complement digital backups. This dual approach ensures data availability even during widespread digital outages.
Offsite storage facilities often feature advanced security measures, such as biometric access and climate control, to safeguard physical backups. Businesses should regularly audit these locations to ensure compliance with safety and security standards.
Integrating Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) with Data Backup
Developing a BCDR Plan: A Step-by-Step Approach
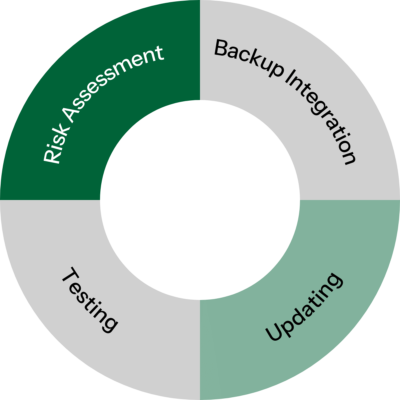
Creating a Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) plan involves:
- Risk assessment: Identifying potential threats
- Backup integration: Ensuring backups align with recovery objectives.
- Testing: Conducting regular drills to validate the plan
- Updating: Revisiting the plan to address evolving risks
A comprehensive business continuity plan must account for various disaster scenarios. Organizations should implement robust corporate data backup systems to ensure continuity during disruptions.
Successful BCDR plans rely on cross-department collaboration. For example, IT teams can work with operations and legal departments to align technical recovery objectives with broader organizational priorities.
The Role of Data Backup in Minimizing Downtime
Downtime can have a devastating impact on small and mid-sized businesses. Recent data suggests that smaller enterprises can lose up to $427 per minute with some incidents leading to annual losses of $1 million when considering both direct and indirect expenses.
Data backup minimizes downtime by enabling rapid restoration of critical systems. Businesses should leverage strategies like incremental backups, which capture only changes since the last backup, to speed up recovery processes.
For industries like healthcare, minimizing downtime is critical for patient care. Rapid data restoration ensures that medical records remain accessible during emergencies, preserving both patient outcomes and organizational reputation.
Security, Compliance, and Legal Considerations in Data Backup
Ensuring Data Security in Backup Processes
Data security is paramount in backup strategies. Best practices include:
- Encryption: Use AES-256 encryption for sensitive data.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Protect access to backup systems.
- Regular audits: Identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Emerging threats like ransomware demand continuous vigilance. Businesses should implement immutable backups—data copies that cannot be altered—to safeguard against malicious attacks.
Navigating Regulatory Compliance in Data Storage and Backup
Compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX dictate how businesses manage data backups, often requiring tailored approaches to meet specific mandates:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Under GDPR, businesses must ensure that personal data is securely stored and backed up. This includes encrypting backups and maintaining clear documentation of backup processes to demonstrate compliance. Additionally, GDPR requires the ability to delete or restore data swiftly to fulfill data subject requests.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): For healthcare organizations, HIPAA mandates the encryption of all backups containing protected health information (PHI). Backup systems must also include robust access controls and logging mechanisms to monitor who accesses or modifies sensitive data.
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): SOX compliance focuses on the integrity of financial records. Companies must ensure that backups of financial data are accurate, tamper-proof, and easily accessible for audits. This often involves implementing version control systems and immutable backups to prevent unauthorized alterations.
Achieving compliance requires meticulous planning, including:
- Encrypting data during transit and storage to safeguard against breaches.
- Keeping detailed logs of backup activities to track changes and access.
- Partnering with compliant backup providers that offer built-in tools for managing regulatory requirements.
Industry-specific compliance challenges, such as maintaining patient confidentiality under HIPAA, require tailored solutions like role-based access controls and periodic security audits. Working with industry experts can streamline compliance efforts, reduce risks of penalties, and ensure that backup processes align with evolving regulations.
Legal Implications of Data Storage and Recovery
Data retention laws vary by region and industry, and compliance with these regulations is critical for avoiding legal and financial penalties. Businesses must:
- Define clear policies for data retention and deletion: Establish standardized protocols specifying how long different types of data should be retained, when they should be deleted, and under what circumstances exceptions apply. For example, GDPR mandates that personal data should not be retained longer than necessary for the purposes for which it was processed.
- Ensure sensitive information, like trade secrets, is securely backed up: This includes encrypting backups to prevent unauthorized access and maintaining an immutable backup copy that cannot be altered or deleted. Industries like finance and healthcare often have specific requirements for safeguarding sensitive data.
- Consider cross-border data storage implications when using international cloud providers: Many regulations, such as GDPR, restrict the transfer of personal data to countries lacking equivalent data protection laws. Businesses must ensure that their cloud storage providers adhere to applicable international data transfer frameworks, such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs).
Failure to comply with these laws can lead to significant fines and reputational damage. For instance, under GDPR, non-compliance fines can reach up to $25 million or 4 percent of global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Partnering with legal advisors and compliance experts can help businesses navigate these complex data storage regulations, ensuring that their backup practices align with both regional and international standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Corporate Data Backup
What should I Look for in Selecting the best backup system for my business?
When choosing a backup system, businesses should:
- Evaluate scalability and integration capabilities: Ensure the system can grow alongside your organization and integrate seamlessly with existing tools and platforms.
- Consider cost versus functionality: Balance the budget with the system’s ability to meet specific business needs, such as rapid recovery or advanced encryption.
- Explore expert recommendations and third-party reviews: Leverage insights from industry leaders and customer experiences to make informed decisions.
Additionally, businesses should prioritize systems that support future technologies, such as AI-driven automation for predictive analytics and automated anomaly detection. These advanced capabilities can help identify potential data issues before they escalate, ensuring a proactive approach to data protection. For example, an AI-enabled backup system can optimize backup schedules based on usage patterns, reducing resource strain while maintaining robust data protection.
What are the Safest Practices for Data Backup?
To ensure reliable backups:
- Avoid relying on a single backup method.
- Conduct regular test restores to verify backup integrity.
- Use robust authentication measures to secure backups.
Engaging employees in regular data protection training can enhance overall backup security by reducing risks of human error.
What are the Optimal Backup Frequency and Strategies?
Determine backup frequency based on data importance. For example, financial transaction logs might require hourly backups, while archived emails might only need monthly updates. Strategic prioritization ensures comprehensive yet efficient coverage.
Advanced tools that analyze data usage patterns can recommend optimal backup schedules, ensuring critical information is prioritized without overloading systems.
Wrapping Up: Key Takeaways and Next Steps in Corporate Data Backup
Summarizing Best Practices in Data Backup
Effective data backup strategies combine cloud and physical solutions, automated schedules, and compliance with regulatory standards. Regular testing and updates ensure readiness for evolving risks.
Actionable Steps for Businesses to Enhance Their Data Backup Strategies
- Assess current backup practices.
- Implement a 3-2-1 strategy.
- Partner with reliable backup providers.
- Regularly review and update BCDR plans.

